The field of Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) has grown dramatically in recent decades, offering hope to millions of couples and individuals struggling with infertility. With medical advances such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), egg donation, surrogacy, and cryopreservation, ART has become a vital part of modern healthcare.
Alongside its clinical importance, the expansion of ART has created a wide range of career opportunities for healthcare professionals, scientists, counselors, and administrative staff. As more people seek reproductive assistance worldwide, demand for skilled workers in this field continues to rise.
This article explores the main ART-related jobs, the skills and qualifications needed, and the future outlook for careers in reproductive medicine.
What Is Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART)?
Assisted Reproductive Technology refers to medical procedures used to address infertility by handling eggs, sperm, or embryos outside the human body. The most common procedure is IVF (In Vitro Fertilization), but ART also includes:
- Egg and sperm donation programs
- Embryo transfer and freezing (cryopreservation)
- Fertility preservation for cancer patients
- Gestational surrogacy
Because ART is highly specialized, it requires a multidisciplinary team of experts. Each role contributes to patient success, making ART careers both rewarding and impactful.
Types of Jobs in Assisted Reproductive Technology
1. Reproductive Endocrinologists (Fertility Specialists)
Reproductive endocrinologists are medical doctors specializing in fertility and hormonal issues. They perform diagnostic tests, develop treatment plans, and carry out IVF and related procedures.
Responsibilities:
- Conduct patient consultations and fertility assessments
- Perform ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, and embryo transfer
- Supervise IVF labs and coordinate with embryologists
- Provide ongoing treatment and follow-up care
Qualifications:
- Medical degree (MD/DO)
- Residency in Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Fellowship in Reproductive Endocrinology
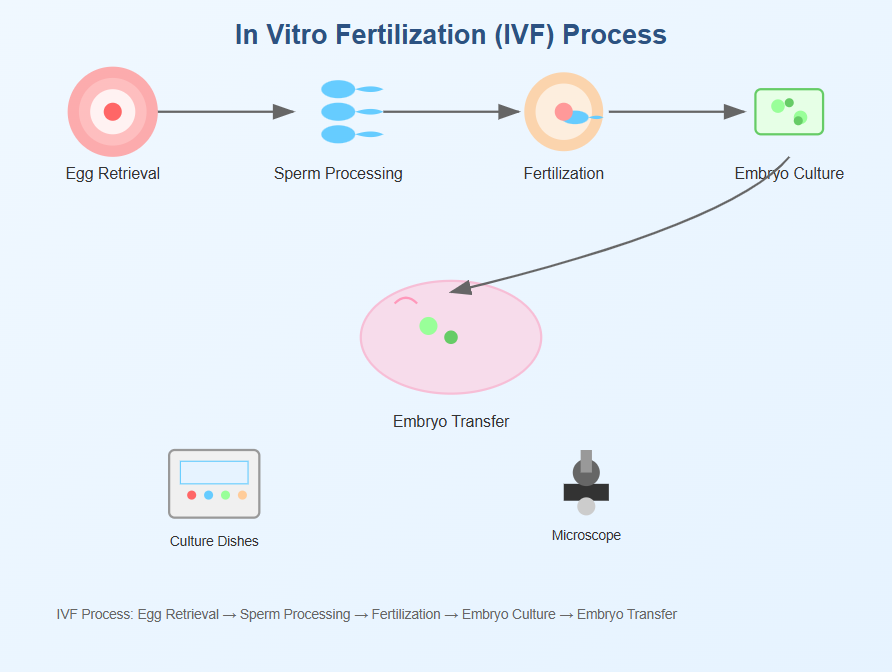
2. Embryologists
Embryologists are at the heart of ART. They work in laboratories to fertilize eggs, monitor embryo growth, and select the best embryos for transfer or freezing.
Responsibilities:
- Handle gametes (eggs and sperm) and prepare for fertilization
- Monitor embryo development using advanced imaging systems
- Conduct ICSI and cryopreservation
- Ensure lab safety and quality control
Qualifications:
- Master’s or PhD in biology, reproductive science, or a related field
- Strong lab and microscopy skills
- Specialized training in embryology techniques
3. Andrologists
Andrologists focus on the male side of infertility, analyzing and treating issues related to sperm health and function.
Responsibilities:
- Perform semen analysis and sperm preparation
- Support sperm retrieval procedures
- Conduct diagnostic tests for male infertility
- Collaborate with embryologists for fertilization processes
Qualifications:
- Degree in biology, biomedical science, or andrology
- Experience with laboratory testing and reproductive biology
4. Fertility Nurses
Fertility nurses are essential in guiding patients through treatment. They provide education, emotional support, and hands-on assistance during ART procedures.
Responsibilities:
- Administer medications and monitor hormone levels
- Educate patients about treatment plans
- Assist doctors during egg retrieval and embryo transfer
- Provide ongoing care and emotional support
Qualifications:
- Nursing degree (BSN or equivalent)
- Training in reproductive healthcare
- Strong communication and empathy skills
5. Genetic Counselors
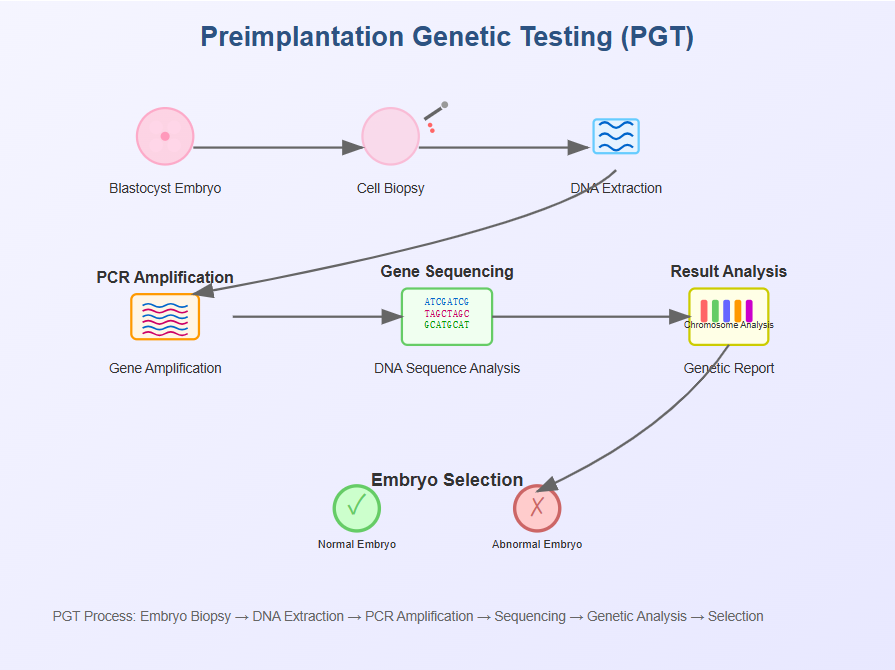
Genetic counselors play an increasingly important role in ART, especially when patients face hereditary risks or consider preimplantation genetic testing (PGT).
Responsibilities:
- Evaluate family medical histories for genetic risks
- Explain genetic testing options to patients
- Support informed decision-making for embryo selection
- Work closely with embryologists and fertility doctors
Qualifications:
- Master’s degree in genetic counseling
- Certification by recognized boards (e.g., ABGC in the U.S.)
6. Mental Health Counselors
Infertility treatments are often emotionally challenging. Mental health professionals provide counseling to help patients cope with stress, grief, and decision-making.
Responsibilities:
- Offer individual or couple therapy
- Support patients during treatment setbacks
- Guide families considering surrogacy or donor programs
- Promote emotional well-being throughout the ART process
Qualifications:
- Degree in psychology, counseling, or social work
- Specialization in fertility or family therapy preferred
7. Laboratory Technicians and Support Staff
ART clinics also require skilled technicians to manage lab operations, maintain equipment, and assist embryologists and andrologists.
Responsibilities:
- Handle lab equipment calibration and maintenance
- Assist in sample preparation and storage
- Ensure compliance with safety and ethical standards
Qualifications:
- Degree or certification in laboratory sciences
- Strong attention to detail and lab safety training
8. Administrative and Patient Care Coordinators
Non-medical roles are also critical. Patient coordinators manage schedules, handle records, and serve as the communication link between patients and clinical staff.
Responsibilities:
- Organize patient appointments and treatment timelines
- Provide information about financing and insurance
- Ensure smooth clinic operations
Qualifications:
- Strong organizational and communication skills
- Background in healthcare administration
Skills Needed for ART Careers
Working in assisted reproductive technology requires both technical expertise and soft skills:
- Scientific knowledge: Deep understanding of biology, genetics, and reproductive systems
- Technical skills: Lab techniques, use of advanced equipment, and diagnostic testing
- Communication skills: Explaining complex treatments in simple terms to patients
- Empathy and compassion: Supporting patients through emotionally difficult journeys
- Attention to detail: ART procedures require precision to maximize success rates

Career Outlook and Job Opportunities
The global fertility industry is growing rapidly. According to industry reports, the ART market is expected to exceed $45 billion by 2030, driven by rising infertility rates, delayed parenthood, and advancements in medical technology.
This growth translates into high demand for professionals across ART roles, from embryologists to fertility nurses. Opportunities exist not only in hospitals and private clinics but also in research institutions, biotechnology companies, and fertility startups.
Countries with the fastest-growing ART sectors include the United States, Europe, India, and China, making this a global career path.
Challenges in ART Careers
While rewarding, ART jobs also come with challenges:
- Emotional stress: Supporting patients facing repeated treatment failures
- Ethical dilemmas: Decisions involving embryo selection, surrogacy, and genetic testing
- Long working hours: Fertility treatments are time-sensitive and often unpredictable
- High training requirements: Many roles demand advanced degrees and certifications
Despite these challenges, ART professionals find their work deeply meaningful, as they help people achieve the dream of having children.
Conclusion
Assisted Reproductive Technology jobs are among the most impactful careers in modern healthcare. From doctors and embryologists to genetic counselors and nurses, every professional plays a vital role in helping individuals and couples overcome infertility.
As technology advances and demand continues to grow, ART careers offer both stability and personal fulfillment. For those passionate about science, medicine, and patient care, this field represents a unique opportunity to combine professional skills with life-changing outcomes.